|
|
- Fall
- The
Planet's opposite sign in exaltation
and has difficulty expressing its true qualities. The planet is
out of its natural element. Example: Mars visiting Cancer.
|
- Feminine
Signs
- Earth
and Water
signs. Feminine refers to receptivity and not gender. Also referred
to as the Negative or Passive signs in some antiquated astrology
texts.
|
Finger
of God
see
Yod |
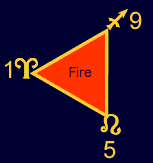
- Fire
Signs
- Aries,
Leo,
and Sagittarius.
These signs are considered fiery, passionate and spontaneous.
In a natural wheel they occupy the first, fifth and ninth houses.
-
|
- Fixed
Signs
- Taurus,
Leo,
Scorpio
and Aquarius.
These signs are associated with fixed and stable emotional characteristics.
The also correspond to the Succedent
houses of the wheel in the Quadruplicities.

-
-
|
- Fixed
Stars
- Stars
that seemed to be fixed in the "vault of heaven." They
form about ninety some constellations.
Examples are the Betelguese, Vega and the stars that make up the
Zodiac.
The appear to move from Earth with the rest of the heavens. As
the heavens move so does this "vault" so they rise in
the East and set in the West.
|
- Flat
Chart or Natural Chart
- A
chart in which the first house is set at zero degrees Aries.
Frequently used when the birth time and therefore the Ascendant
is not known.
|

|
|
- Geocentric
- 1)
The most commonly held view in astrology, regarding the positions
of the observer on the Earth as center of the cosmos, in contrast
to the heliocentric
view of the world, which is the sun as the center. 2) In reference
to latitude, refers to using measurements based on the angle formed
at the Earth's center between the line extending to the surface
at the location and the line extending to the surface at the equator.
(This can vary from geographic latitude by as much as 12 minutes.)
|
- Grand
Cross (also know as Grand Square)
- Planetary
configuration between four planets that are made in a native's
chart. Two pairs of planets are opposite each other (180 degrees)
thus all four planets are squared (90 degrees) to the other. See
illustration. Read
ARTICLE
-
|
- Grand
Trine
- Planetary
configuration between three planets that made in a native's chart.
All three planets are 120 degree from each other. See illustration. Read ARTICLE
|
- Greater
Benefic
- Jupiter.
Assumed to bring you major blessings. Used in Classical
Horary Astrology
|
- Greater
Malefic
- Saturn.
Assumed to be the cause of stress and strain in your life. Used
in Classical Horary Astrology
|
- Gregorian
Calendar
- The
Calendar used in general by the world nowadays. Introduced by
Pope Gregory XIII as a revision of the Julian
Calendar in 1582.
|

|
|
- Hard
Aspects
- Inharmonious
aspects. Generally considered to be the Squared
and Opposition
and others. Aspects
when the energies do not always help.
|
- Harmonics
- The
astrological study of integral division of the circle. For example:,
by 2, 3, 4, 5 and etc. The aspect Quintile
is considered the 5th harmonic.
|
- Harmonious
Aspects
- Conjunct,
Sextile
and Trine.
Also referred to as the Soft aspects
or Easy aspects.
|
- Heliocentric
- 1)
The view of the universe, according to the modern knowledge, with
the Sun
 as the center of our
planetary system. 2) The practice of erecting the chart by using
the Sun as the viewpoint thus having instead of a SUN sign the
individual would have an EARTH Sign as the center of our
planetary system. 2) The practice of erecting the chart by using
the Sun as the viewpoint thus having instead of a SUN sign the
individual would have an EARTH Sign .
The further away a planet is from the Sun the less its geocentric
position varies. The inner planets Mercury and Venus can be 180°
in variance. .
The further away a planet is from the Sun the less its geocentric
position varies. The inner planets Mercury and Venus can be 180°
in variance.
|
- Horary
- This
is the practice of answering questions through the horoscope at
the time the question was asked. Horary means "by the hour".
The chart would be cast for the moment the question was given
birth in the person's mind or asked of the astrologer. There are
modern horary practices but much would not exist without the pioneer
efforts of the 17th century gentleman, William Lilly, 1602-1681.
To learn more about horary astrology, visit the English
Merlin.
-
|
- Horoscope
- A
diagram of the map of the heavens at a particular time of an event
(birth or another event). It contains the representation of the
luminaries
(Sun and Moon) and the eight planets viewed from he place of the
event. The horoscope simultaneously records two movements of the
heavenly bodies. First, the movement of the planets and luminaries
through the Zodiac
and second, the movement of the Zodiac around the Earth.
|
- House
- A
section of the Zodiac, mathematically defined, which represents
a particular area of life. The four quadrants which result from
the system of axes are each subdivided into three fields. The
calculation of the system axes is identical in almost all the
various schools of Astrology the method of subdividing differs.
See House
System. The resulting houses correspond to the twelve signs
of the Zodiac but are not identical. For more information go to
this page.
-
|
-
- House
Cusp
- A
House Cusp
is the dividing line between Houses on the Zodiac
Wheel. When a planet is said to be in a House Cusp, this means
that the planet is positioned on this dividing line, therefore
giving the planet influence over two adjoining houses.
|
- House
System
- The
way of dividing the houses varies according to the method used.
The best-known are the Koch
(developed by Dr. Walter Koch), Placidus
(developed by Placidus de Titus), Campanus
(developed by Giovanni Campani) and Regiomontanus
(developed by Johannes Muller) and Equal
House.
|
|
|
-
IC
- See
Imum
Coeli
|
- Imum
Coeli
- The
bottom of the heavens. The fourth
house cusp in non-equal or Quadrant
House System. Represent the family relations and the home
life. Also known as the Nadir.
|
- Ingress
- The
simple definition is entrance. In astrology, this refers to the
entrance of planets into the twelve houses as denoted on the ephemeris.
-
|
- Interception
- 1)
A sign that falls between two adjacent house
cusps, but neither of those house cusps are in that sign.
Since most House divisions are unequal, at some latitudes it is
quite common to have a chart where two opposite signs are entirely
contained within houses, so that no degree of either sign appears
on a House Cusp. In such a chart, two other opposite signs will
appear on two house cusps each.
-
- Interceptions
emphasis are more of the houses where the signs are playing double
duty (eg. 1st and 2nd house Leo and 7th and 8th house Aquarius).
The interpretation focus would be on where the ruling planets
of those signs (in the example above: the Sun and Saturn) is in
the native's chart and what aspects it forms to other key planets
and points.
-
-
2) A planet that is in a degree of the
sign that is intercepted (contained within a house and not a cusp)
is said to be intercepted itself. Some astrologers then interpret
that planet's energies to be blocked in expression.
See
illustration of a Natal Chart that has an interception
|
 |
|
- Julian
Calendar
- A
calendar introduced in Rome in 46 B.C.E. Established a year of
365 days with every fourth year having 366 days.
|

|
|
- Kite Configuration
- read
article
|
|
- Koch
- Dr.
Walter Koch (pronounced 'coke'), a German astrologer who found
the Koch House
System or Birthplace House System.
|
|
|
- Latitude
- 1)
Celestial: Angular distance North or South of the ecliptic—measured
in degrees, minutes and seconds. 2) Terrestrial: Angler distance,
north or south of the equator—measured in degrees, minutes
and seconds.
|
- Local
Sidereal Time
- The
time of birth at the birthplace, converted to sidereal (star)
time. It is the hour angle of the vernal point (0° Aries).
This is the figure from which the house cusps of the chart are
derived.
-
-
|
- Longitude
- 1)
Celestial: Angular distance, measured in degrees, minutes and
seconds—east of 0° Aries, along the ecliptic. Astologers
are using Celestial Longitude when they speak of House positions
or planetary position in signs. 2) Terrestrial: Distances measured
east and west—in degrees, minutes and seconds. The 0°
point is the Prime Meridian
at Greenwich, England
|
- Luminaries
- The
luminaries are the Sun and Moon. Often Astrology speaks of ten
planets
which include the luminaries of the Sun and the Moon even though
they are not technically planets.
|